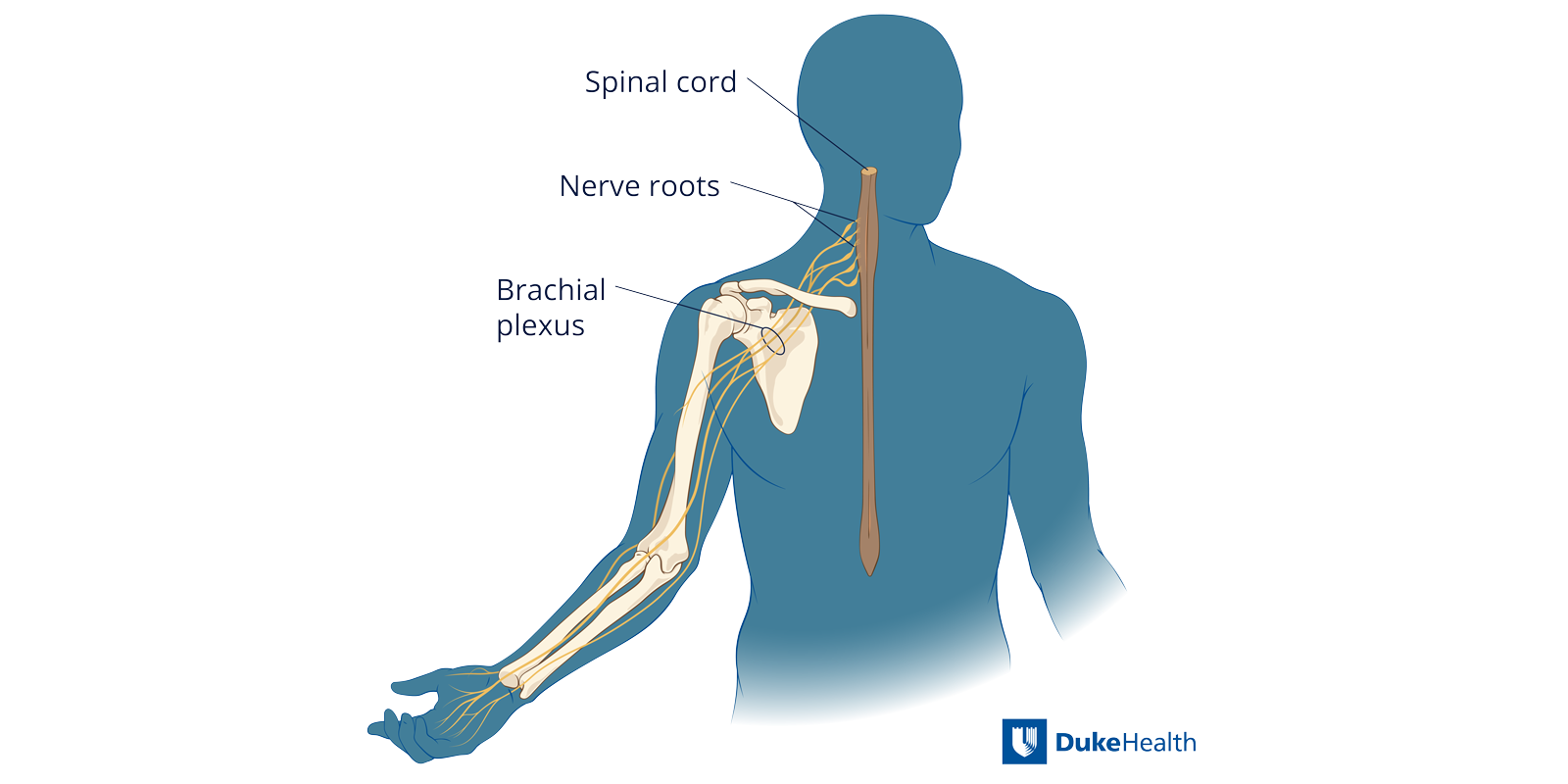
What Is the Brachial Plexus?
The brachial plexus is a network of peripheral nerves that transmit signals among your brain, spinal cord, arm, and hand. Signals travel from the spinal cord to stimulate muscle movement, while signals travel from the arm to the spinal cord and brain to relay sensory information.
Brachial Plexus Injury
A team of Duke experts collaborates to care for adults with brachial plexus injuries -- damaged nerves in the shoulder, arm, and hand. We offer the full range of treatment options, from highly specialized physical and occupational therapy to the most advanced approaches in neurosurgery, plastic surgery, and orthopaedic surgery. We advocate for early assessment and treatment to help you avoid chronic pain and restore sensory and motor function.
About Brachial Plexus Injury
Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries
There are several types of brachial plexus injuries:
- Brachial plexus stretch occurs when the nerves near the spinal cord are stretched. People with stretch injuries often experience weakness, numbness, and sometimes pain that radiates down one arm.
- Brachial plexus rupture occurs when the nerves partially or fully tear outside of the spinal cord. This can cause a range of sensory and motor problems as well as pain that may or may not require surgery.
- Brachial plexus avulsion occurs when the nerve roots tear away from the spinal cord. Avulsions are the most severe type of brachial plexus injury and can cause severe pain and permanent loss of function, requiring more advanced reconstructive techniques.
Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
The most common cause of brachial plexus injuries is trauma from things like high-speed impacts, athletic injuries, knife and gunshot wounds, or vehicle accidents. Tumors, radiation, and surgery can also damage the brachial plexus.
Duke Health offers locations throughout the Triangle. Find one near you.
Brachial Plexus Injury Tests
Your doctors will perform a thorough physical exam to assess your motor function, sensory deficits, and areas of pain. They may also recommend one or more of the following tests:
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies
Neurologists use electrodes -- either surface electrodes placed on the skin or needle electrodes inserted into a muscle -- to stimulate nerves and record electrical activity in the muscle.
Imaging Scans
CT, MRI, X-ray and/or ultrasound scans can show brachial plexus injuries and related problems in detail, as well as surrounding bone or soft-tissue injuries and scar tissue.
Brachial Plexus Injury Treatments
Your doctors will consider many factors -- including your injury type, severity, symptoms, and time since the injury occurred -- to create a customized treatment plan to meet your needs. Less severe brachial plexus injuries may heal with conservative treatment. More complex injuries that involved greater nerve damage may need surgery.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy: Research shows that people with brachial plexus injuries who start physical and occupational therapy early have better overall outcomes, whether or not surgery is needed. This is because physical and occupational therapy help preserve joint mobility and strength. Our highly specialized outpatient rehabilitation program helps you preserve function in your arm and hand and prevent complications like contractures (when tendons shorten from lack of use) and joint stiffness.
- Pain management: Medications, creams, and injections can reduce pain.
Surgical Treatments
Depending on the type of injury, surgery to repair brachial plexus injuries is most effective when it occurs within six to 12 months of the initial injury. After surgery, physical and occupational therapy as well as maintaining good mental health, are vital to maximizing function and re-training the brain to use new nerve or muscle tissue. These are the main types of surgery that restore function and reduce pain:
- Neurolysis: Surgeons loosen and remove scar tissue around the damaged nerve to restore function.
- Nerve graft: Surgeons remove a small section of a damaged nerve and replace it with a section of nerve harvested from another part of your body, usually the leg, or from a cadaver.
- Muscle transfer: During this technique, also called free functioning muscle transfer, surgeons identify a working muscle in another area of your body and move it to the location in your arm that is not working to restore a specific function (for example, bending the elbow).
- Nerve transfer: Surgeons move a portion of a damaged nerve that is close to the weak or paralyzed muscle and connect it with a functioning nerve.
Dorsal Root Entry Zone (DREZ) Lesioning
DREZ lesioning is a surgical procedure that reduces pain in the shoulder, arm, and hand due to brachial plexus avulsions. The DREZ procedure was pioneered at Duke, and we are the only center in North Carolina, and one of the few in the U.S., offering this advanced treatment option.
Best Hospital for Orthopaedics, Neurosurgery in NC
Where you receive your care matters. Duke University Hospital is proud of our team and the exceptional care they provide. They are why our orthopaedics, neurology, and neurosurgery programs are nationally ranked and are the highest-ranked programs in North Carolina, according to U.S. News & World Report for 2025–2026.
Why Choose Duke
Expert Team Approach to Care
From diagnosis through surgery and beyond, every step of your care is managed by highly trained peripheral nerve experts who help you maximize your shoulder, arm, and hand function. Our occupational therapist is specifically board-certified in hand therapy, and our neurosurgeons, plastic surgeons, and orthopaedic surgeons are fellowship-trained in peripheral nerve surgery. We also collaborate with specialized neurologists, physiatrists, and pain psychologists who are highly experienced in diagnosing and treating these injuries and creating comprehensive care plans within our specially designed nerve health program.
Brachial Plexus Thought Leaders and Researchers
Many of our providers participate in peripheral nerve organizations and attend national conferences to learn about the latest advances in the field and present research. Our researchers are always working to better understand brachial plexus injuries and find new and better ways to treat them.